
Foshan Fulan Laser Technology Co., Ltd.
National Hotline: 0757-29899345
Manager Wen: 18902563402
Fax: 0757-29899345
Business QQ: 2801827697
E-mail: china@fsfulan.com
Address: No.14, Leliu Port Intensive Industrial Zone, Shunde District, Foshan CityThe high-tech zone almond altar town, shunde, foshan city shun industry west road no. 15 cimc valley 20 9 / f, building B
No matter how good and advanced the equipment is, sometimes due to the influence of external factors, the processing quality is poor, and the laser welding machine is no exception. Next, Foshan Fulan Laser will briefly talk about the main reasons that affect the quality of laser welding.
1. Welding equipment
1. Laser type: The laser of laser welding machine mainly includes pulse laser and continuous laser. The corresponding material should use the corresponding laser type.
2. Beam mode: The lower the beam mode order, the better the beam focusing performance (that is, the better the beam quality), the smaller the spot, the higher the laser power density under the same laser power, and the larger the welding aspect ratio.
3. Output power stability: The better the output power stability of the laser, the better the welding consistency.
4. Light guide and focusing system: Under the action of high-power laser, the performance of these optical parts may be deteriorated, the transmittance will decrease, and the thermal lens effect (the focal length of the lens will change when it is heated). If there is surface contamination, it will increase transmission loss and may even cause damage to optical parts. Therefore, the quality, maintenance and working condition monitoring of optical parts are essential to ensure the quality of welding.
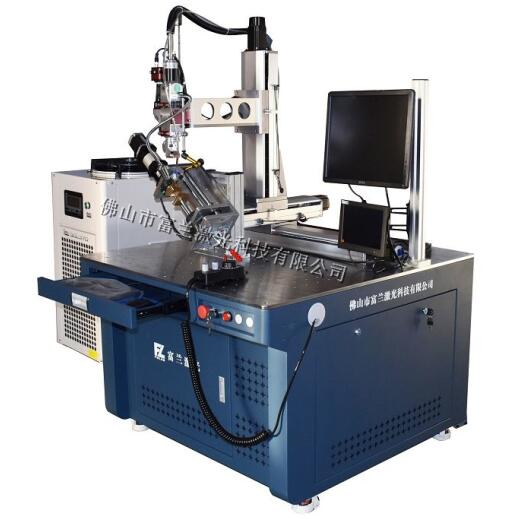

Two, welding workpiece
1. Absorption rate of the material to be welded: The compatibility of the absorption of the laser beam and the material depends on some important properties of the material, such as absorptivity, reflectivity, thermal conductivity, etc., among which the most important is the absorption rate. Some materials are particularly good for laser absorption, while some materials are very poor and even do not absorb.
2. The uniformity of the required welding workpiece material: the uniformity of the material directly affects the welding quality. For example, when aluminum alloy materials are welded, if the distribution of alloy elements is uneven, or the content of impurities inside is different, welding defects such as blast holes, undercuts, and depressions are prone to occur; another example is uneven material size (especially thickness and height). It will not fit the fixture and deviate from the focal length of the welding head, which will also lead to poor welding quality.
3. Assembly accuracy of welding workpiece: Because the laser spot is small and the welding seam is narrow, filler metal is generally not added. If the assembly gap is too large, the beam will pass through the gap and cannot melt the base material, or cause obvious undercuts and dents.
4. The cleanliness of the workpiece to be welded: If the surface is not clean and there are impurities, it will also cause poor welding quality.
Three, welding fixture
Most products need to use fixtures (also called: tooling, jigs) when welding. The fixture is mainly used to accurately locate and reliably clamp the workpiece to be welded, which facilitates the assembly and welding of the welded workpiece, ensures the accuracy of the welding structure, and effectively prevents and reduces welding deformation. Therefore, the quality of the fixture will directly affect the quality of welding.
Four, welding process parameters
The welding process parameters mainly include laser output power, welding speed, laser waveform, pulse frequency, defocusing amount and shielding gas.
1. Output power stability: The better the output power stability of the laser, the better the welding consistency.
2. Welding speed: the higher the welding speed, the shallower the penetration. The molten pool at low speed is large and wide, and it is easy to collapse. During high-speed welding, the liquid metal in the center of the weld is too late to redistribute, and it solidifies on both sides of the weld, forming an uneven weld. Therefore, Foshan Fulan Laser recommends that you use high-speed welding when welding thin plates or materials with better weldability; low speed for thick plates and difficult-to-weld materials.
3. Laser waveform: The laser waveform mainly includes the pulse waveform commonly used by pulse lasers and the seam welding waveform during continuous welding. For example: when welding copper, aluminum, gold, and silver highly reflective materials, in order to break through the barrier of high reflectivity, trapezoidal laser waveforms can be used; for ferrous metals such as iron and nickel, where the surface reflectivity is low, rectangular waves or slow attenuation should be used Waveform.
4. Pulse frequency: The pulse frequency, spot size and welding speed are matched with each other to achieve the required overlap rate. Generally speaking, the greater the overlap rate, the smoother the weld, but the welding speed also decreases accordingly. When the laser pulse frequency exceeds a certain value, the overlap rate is too large, exceeding the welding limit of the material, and it is easy to weld through or appear welding slag.
5. Defocus: There are two defocus methods, positive defocus and negative defocus. If the focal plane is above the workpiece, it is a positive defocus, otherwise it is a negative defocus. Under negative defocusing, the power density inside the material is higher than that on the surface, and it is easy to form stronger melting and vaporization, so that the light energy can be transmitted to the deeper part of the material. Therefore, in practical applications, when the penetration depth is required to be large, the negative defocus is used; when the thin material is welded, the positive defocus should be used.
6. Pulse width: This is mainly for laser welding machines for pulsed lasers. Pulse width is one of the important parameters of pulsed laser welding machines. It is not only an important parameter different from material removal and material melting, but also determines the cost and volume of processing equipment key parameter. The longer the pulse width, the larger the diameter of the solder joint, and the deeper the penetration at the same working distance.
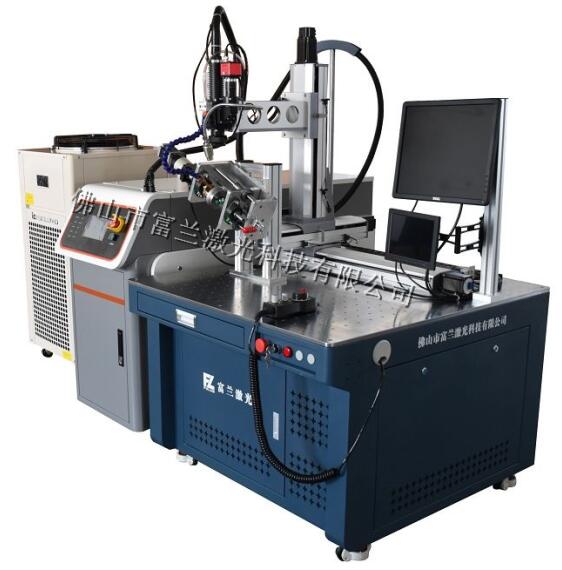

Five, workbench
The workbench will directly affect the processing efficiency and the welding effect. The energy feedback fiber optic transmission laser welding machine produced by Foshan Fulan Laser has flexible placement, the host and the workbench are separated, and there are a variety of workbenches to choose from, and different workbenches can be configured for welding according to the needs of different products.
Six, protective gas
Shielding gas is also one of the important factors affecting welding quality. Shielding gas is an inert gas used to protect the molten pool during laser welding. Some materials can be welded without considering the surface oxidation without shielding gas, but for most applications, shielding gas is required. Because the shielding gas can drive or weaken the plasma (plasma is easily generated in the laser welding process, and the plasma can absorb, refract and reflect the laser), increase the cooling rate of the weld, reduce the degree of oxidation of the weld surface, and improve the welding Seam surface morphology and other effects. Commonly used protective gases include nitrogen, argon, helium, and a mixture of argon and helium.